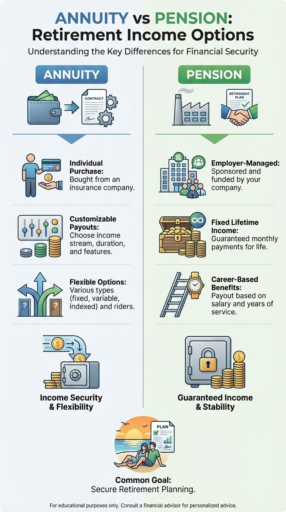
An annuity lets you convert your savings into customizable payouts, while a pension guarantees a fixed benefit based on your career and salary history.
Annuities vs pension is a crucial retirement choice, with the main difference in control and predictability.
This article covers:
- Are an annuity and pension the same thing?
- What’s the difference between an annuity and a pension?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of an annuity and pension?
- What are the tax implications of annuities and pension?
Key Takeaways:
- An annuity delivers predictable income and can be purchased through a retirement account.
- A pension provides employer-managed, career-based income.
- Annuities are flexible but may have fees; pensions are simpler but less portable.
- Tax implications for both should be understood for effective retirement planning.
My contact details are hello@adamfayed.com and WhatsApp +44-7393-450-837 if you have any questions.
The information in this article is for general guidance only. It does not constitute financial, legal, or tax advice, and is not a recommendation or solicitation to invest. Some facts may have changed since the time of writing.

Annuities vs Pensions: The Right Comparison Framework
Although annuities and pensions are often compared as similar retirement income tools, they are designed to solve different problems.
A pension is structured to provide foundational income that is guaranteed and managed by an employer or pension authority, with limited control over payout design.
An annuity, by contrast, allows individuals to convert their own savings into income, offering flexibility in payout timing, duration, and beneficiary options.
The most useful way to compare annuities and pensions is not by asking which is better, but by examining who controls the income, how predictable the payments are, and how each fits into an overall retirement plan.
This framework helps clarify why pensions often form the base of retirement income, while annuities are commonly used to supplement or customize it.
What is an annuity and how does it work?
An annuity is a financial contract with an insurance company in which you pay a lump sum or a series of payments in exchange for future income.
The structure can vary: annuities may be fixed (guaranteed payout), variable (payments depend on investment performance), or indexed (linked to a market index with some guaranteed minimum).
Annuities can begin payments immediately (immediate annuities) or at a future date (deferred annuities), and they may include options for lifetime income, period certain payouts, or beneficiary protections.
The contract is designed to turn retirement savings into a structured income stream, giving retirees predictable or semi-predictable payments depending on the product type.
What is a pension and how does it work?
A pension is an employer-sponsored retirement plan that promises to pay a retiree a specific benefit, usually based on salary history and years of service.
Pensions are typically defined benefit plans, meaning the employer guarantees a fixed monthly payment upon retirement.
Some pensions are defined contribution plans, where contributions are made by the employer (and sometimes the employee) into an individual account, and retirement income depends on the account balance at retirement.
Pensions are generally managed by the employer or a pension fund, which handles investments and disbursements, relieving the employee of ongoing investment decisions.
The payments are usually made monthly and may continue for the retiree’s lifetime, sometimes including survivor or spousal benefits.
What is the difference between a pension and an annuity?
The key difference is that pensions offer fixed, employer-guaranteed income, while annuities convert your own savings into a customizable income stream.
- Pensions provide a fixed retirement benefit determined by your salary and years of service, typically paid monthly for life.
- Annuities are purchased with your own funds and can offer lifetime payments, fixed terms, or variable growth depending on the product.
In short, pensions deliver guaranteed employer-backed income, whereas annuities are individually purchased and can supplement retirement funds.
Do you need an annuity if you have a pension?
Not necessarily. A pension already provides steady retirement income.
An annuity may be added to supplement income, cover gaps, or provide additional benefits, such as survivor payouts or inflation protection.
Which is better, retirement annuity or pension fund?
A pension fund is better for baseline retirement security, while a retirement annuity is better for filling income gaps and increasing flexibility.
A pension works best as a core income source because payments are fixed and continue for life, covering essential living expenses.
A retirement annuity is typically used to supplement that base income, allowing retirees to adjust payout timing, duration, or beneficiaries.
In practice, pensions suit retirees who want simplicity and predictability, while annuities are more useful for those planning around early retirement, uneven income needs, or legacy goals.
Combining both can improve income planning without duplicating benefits.
Does a pension count towards taxable income?
Yes, in many countries, pension income is taxed as ordinary income when it is received.
This applies in jurisdictions such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, and most of Europe, where pensions funded with pre-tax contributions are taxable at payout.
In some jurisdictions, pension benefits may be fully or partially exempt from income tax.
Certain countries in Asia, the Middle East, and select retirement schemes provide tax exemptions for qualified retirees, and investment income earned within pension funds is often tax-exempt while it remains inside the fund.
In all cases, the tax treatment depends on local pension laws, how contributions were made, and whether exemptions apply at retirement.
Do you have to report an annuity on a tax return?
Yes, annuity payments generally must be reported on your tax return.
In jurisdictions such as the United States, annuity income is reportable whether it comes from a retirement account or a personally purchased annuity.
Reporting rules may differ in other countries.
How are you taxed on an annuity?
Annuity income is taxed based on how the annuity was funded.
Annuities held inside retirement accounts are taxed as ordinary income when withdrawn.
Annuities purchased with after-tax money are taxed only on the earnings portion of each payment, while the original principal is not taxed.
What are the advantages of pension vs annuity?
Pensions provide dependable lifetime income through employer-sponsored plans, requiring minimal decision-making and often including survivor benefits, which ensures a stable foundation for retirement.
Annuities give retirees flexible, customizable payouts and are portable if purchased individually, allowing income to be adjusted to meet changing retirement needs or goals.
What are the disadvantages of a pension vs annuity?
Pensions offer limited control over investments, are generally not portable if you change employers, and may provide income that is fixed and may not keep pace with inflation, which can restrict financial flexibility in retirement.
Annuities can involve higher fees and surrender charges, may deliver lower growth compared with market-based investments, and can be complex to understand, making it challenging for retirees to navigate all contract features.
Conclusion
Annuities and pensions each play distinct roles in retirement planning: pensions provide the bedrock of financial security, while annuities offer opportunities to adapt income to changing needs, manage longevity risk, and create a potential legacy.
The real insight lies in understanding how these tools interact.
Using a pension as a reliable foundation while strategically layering annuities can give retirees both confidence and control, helping them navigate market fluctuations, inflation, and life’s uncertainties with greater peace of mind.
FAQs
What are the four types of annuities?
The four main types are fixed, variable, indexed, and immediate annuities, each offering different income strategies and risk levels.
Is a Roth IRA considered an annuity?
No, a Roth IRA is not an annuity. It is a retirement account allowing after-tax contributions with tax-free growth and withdrawals.
However, you can hold certain annuities inside a Roth IRA, combining tax-free growth with structured payouts.
Is a pension annuity taxable income?
Yes, most pension annuities are taxed as ordinary income when payments are received.
Can I withdraw 100% of my pension fund?
Some pension plans allow a lump-sum payout of the full fund, while others provide only monthly installment payments.
Early withdrawals may incur penalties or reduce future benefits, so the available option is determined by your specific pension rules.
Pained by financial indecision?

Adam is an internationally recognised author on financial matters with over 830million answer views on Quora, a widely sold book on Amazon, and a contributor on Forbes.



