When comparing annuities vs CDs, the core distinction is how each generates income and manages risk.
CDs are bank-issued time deposits with fixed interest rates and insured principal, while annuities are insurance contracts designed to provide predictable income, often for retirement.
This article covers:
- How do annuities differ from CDs?
- What is the biggest disadvantage of an annuity vs CD?
- Is an annuity a safe investment?
- Are CDs considered safe investments?
- Why are annuity rates so high?
Key Takeaways:
- CDs offer principal protection and guaranteed interest but limited growth potential.
- Annuities provide higher income and longevity protection but rely on insurer strength.
- Annuities carry fees and limited liquidity; CDs are simple and liquid after maturity.
- Many investors use both as part of a balanced, income-focused strategy.
My contact details are hello@adamfayed.com and WhatsApp +44-7393-450-837 if you have any questions.
The information in this article is for general guidance only. It does not constitute financial, legal, or tax advice, and is not a recommendation or solicitation to invest. Some facts may have changed since the time of writing.

What is the difference between a CD and an annuity?
The main difference between a certificate of deposit (CD) and an annuity is that a CD guarantees interest on a fixed deposit, while an annuity provides a stream of payments that can last for life.
A CD is a bank product where you deposit a fixed amount for a set period in exchange for guaranteed interest.
Your principal is typically insured up to regulatory limits (e.g., FDIC in the US).
An annuity, in contrast, is an insurance contract that converts a lump sum into a stream of payments, either immediately or at a future date.
Payments can continue for a fixed term or for life.
Unlike CDs, annuities are not insured by the FDIC, and their guarantees depend on the financial strength of the insurer.
Why do annuities pay more than CDs?
Annuities pay more than CDs because they take on additional risks and invest in higher-yield assets to provide guaranteed income.
- The insurance company assumes longevity risk, meaning payments continue even if the investor lives longer than expected.
- Investment portfolios backing annuities often include higher-yield assets than the ultra-safe, low-return assets typically used to fund CDs.
- Annuities may have longer investment horizons, allowing insurers to generate higher returns and pass some of that to the annuitant.
Are CDs better than annuities?
CDs are better for short-term or flexible savings needs, while annuities are better for long-term income planning.
CDs work well for investors who want a simple place to park money for a defined period or maintain funds for near-term goals.
Annuities are more appropriate when the objective is to convert savings into a predictable income stream, particularly later in life.
The better option depends on whether the goal is temporary cash management or long-term income structuring, rather than overall safety.
Are annuities safer than CDs?
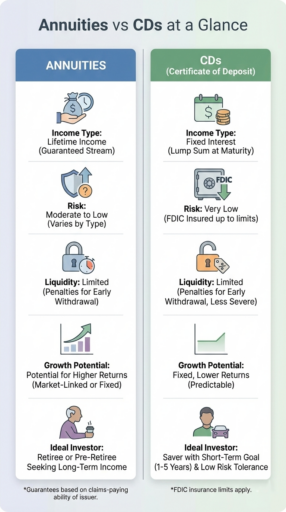
Annuities are safer for guaranteed income, while CDs are safer for protecting principal.
CDs offer strong principal protection because deposits are insured up to regulatory limits.
Annuities offer income security through contractual guarantees, but rely on the financial strength of the insurer rather than deposit insurance.
In practice, CDs protect capital, while annuities protect cash flow, making their safety profiles fundamentally different rather than directly comparable.
What are the pros and cons of annuities vs CDs?
In general, CDs offer safety and simplicity at the cost of lower returns, while annuities provide stronger income guarantees but introduce liquidity limits, fees, and insurer risk.
Advantages of CDs
- Principal is typically insured up to regulatory limits, supporting capital preservation.
- Interest is fixed for the term, making outcomes predictable.
- CDs are easy to understand and require minimal ongoing management.
Disadvantages of CDs
- Yields are often low and may not keep up with inflation.
- Early withdrawals usually trigger penalties.
- CDs do not generate lifetime income.
Advantages of annuities
- Annuities can deliver higher income payouts, particularly over longer horizons.
- They can guarantee income for life or for a defined period.
- Annuities help manage the risk of outliving savings.
Disadvantages of annuities
- Access to principal is restricted, especially during surrender periods.
- Fees and contract features can reduce net returns.
- Guarantees depend on the insurer’s financial strength rather than government-backed insurance.
Should I get an annuity or a CD?
Choose a CD if your priority is preserving cash for a known future use, and choose an annuity if your priority is turning savings into sustained income later in life.
You should consider:
- Time alignment: CDs work best when funds are earmarked for a specific date, while annuities are designed to convert assets into long-duration payouts.
- Cash-flow structure: Annuities create scheduled income, whereas CDs function as holding vehicles rather than income engines.
- Risk trade-offs: CDs limit downside but cap upside, while annuities accept insurer exposure in exchange for income stability.
- Portfolio role: Many investors pair CDs as short-term stabilizers with annuities as long-term income foundations.
Conclusion
Annuities and CDs are often compared as if one must replace the other, but they serve different roles in how money behaves over time.
CDs keep capital intact and available, while annuities reshape capital into income with a defined purpose.
The more useful question is not which is better, but where certainty matters most at the point of deposit, or at the point of payout.
When chosen deliberately, each can reduce a different kind of financial stress rather than compete for the same role.
FAQs
Why do financial advisors not like annuities?
Financial advisors sometimes avoid recommending annuities due to high fees, complex terms, and limited liquidity, which can reduce overall investment flexibility.
How much does a $100,000 CD make in a year?
A $100,000 CD earning 4% would generate about $4,000 in interest over one year.
The exact amount varies with the stated rate and term, with interest usually paid monthly, quarterly, or at maturity.
What are the similarities and differences between savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs) and money market accounts?
Savings accounts, CDs, and money market accounts are all low-risk bank products, typically insured by the FDIC up to regulatory limits, and provide interest on deposited funds.
The key differences lie in liquidity and interest structure: savings accounts are highly liquid with variable interest rates, CDs offer fixed interest for a set term but penalize early withdrawals, and money market accounts usually provide higher interest than savings while limiting the number of transactions.
What is the difference between annuity and FD?
A fixed deposit (FD) or CD is a bank product with guaranteed principal and interest, while an annuity is an insurance contract that provides a structured income stream, potentially for life, and depends on the insurer’s solvency.
Pained by financial indecision?

Adam is an internationally recognised author on financial matters with over 830million answer views on Quora, a widely sold book on Amazon, and a contributor on Forbes.



